What is creatine? - Everything you need to know!

The first creatine (creatine, creatine) monohydrate came onto the market in the mid-1980s. At first, a few grams of the new wonder substance cost several hundred euros. Today, creatine research has come a long way and is constantly providing us athletes with new creatine supplements that are designed to increase our performance and muscle growth. Today we already count over a dozen different types of creatine. Starting with the normal monohydrate to new creatine formulas like the Kre-Alkalyn.
Creatine is mainly ingested through food and is mainly found in fish or meat. Our body itself can only produce a small amount. More than 90% of the creatine absorbed by the body or produced by the body is stored in the skeletal muscles.
In the body, creatine is mainly formed in the liver. The body needs the following amino acids for the formation of this carbon-nitrogen compound: L-glycine, L-methionine and L-arginine. From these he can synthesize creatine. Stored in skeletal muscle, it serves as the primary source of energy.
Creatine is a purely natural substance
However, for use in dietary supplements, creatine must be chemically synthesized.
One of the successes of creatine is certainly the fact that there are almost no known side effects, as long as you follow certain rules regarding intake and use.
What does creatine do
To understand how creatine works, one must first understand how energy production works in the body. It takes its energy from three sources: ATP, glycogen and fat. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary and also the fastest source of energy. It can be made available quickly by the body and is decisive for rapid and maximum strength.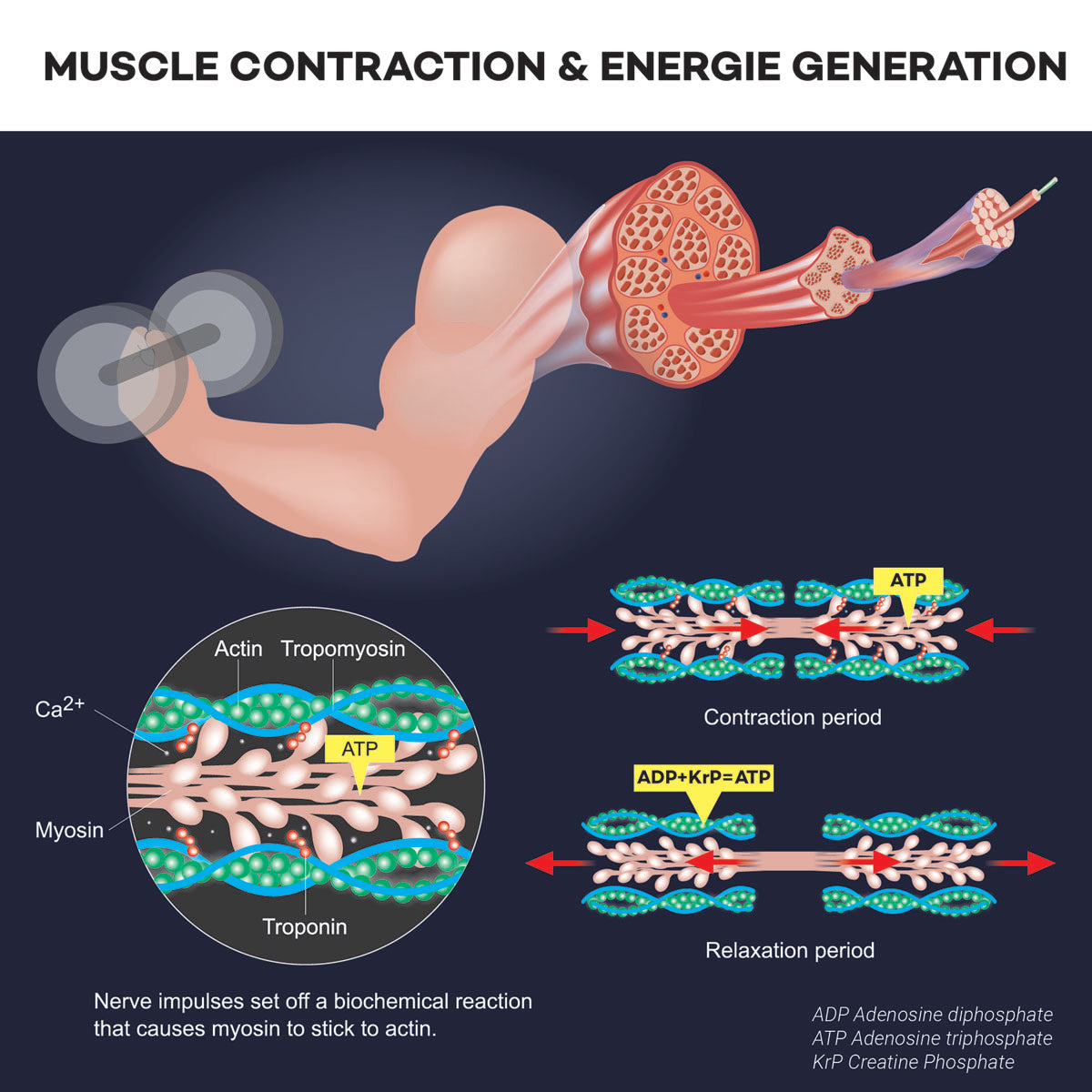
However, the ATP memory is very limited and exhausted after just a few seconds. The ATP decomposes here to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), so it loses a phosphate molecule. Here the body now uses the stored KrP (creatine phosphate) by synthesizing energy-rich ATP from ADP and KrP.
Muscle energy formula: ADP + KrP = ATP
Creatine thus serves as the main source of energy in the muscle, which acts directly in the muscle tissue and supplies the necessary energy for muscle contractions there. During short, intense exertions that require a high level of strength, the stored KrP is used as the first source of energy. However, the storage capacity of the muscles, the so-called creatine storage, cannot be expanded at will. It is limited to a certain amount, beyond which the muscle can no longer absorb any more creatine.
The more creatine phosphate stored in the muscle, the more energy it can use for muscle contractions.
By delivering energy directly to the muscle, creatine promotes strength, muscle growth and recovery like almost no other ingredient.
Creatine types at a glance
- Creatine AKG
With this creatine, another molecule is attached to the creatine with alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG). The additional molecule is said to improve the bioavailability and absorption of creatine. This should help athletes who do not react to creatine, so-called non-responders, to increase the creatine stores in the muscles.
- Creatine HCL
With this creatine, another molecule is attached to the creatine with hydrochloride (HCL). A creatine salt is formed. This has a much higher solubility than the previous creatine molecule and therefore a theoretically higher bioavailability. The following advantages are associated with creatine HCL: It requires less water for transport and storage in the muscle; you need a smaller dosage than regular creatine monohydrate.
- Creatine Monohydrate
The forefather of all types of creatine is the classic creatine monohydrate. Creatine monohydrate is a fine white powder and can be manufactured into a variety of forms including tablets, capsules, chewable tablets and powder. Of all creatine varieties, it is considered the best and most researched form of creatine in the world and is still the first choice for many athletes and strength athletes today. Hardly any other performance-enhancing substance has been researched as thoroughly as creatine monohydrate.
- Creatine Alkalyn
This creatine is combined with basic powder to make it more resistant to aggressive stomach acid. If the creatine stays in the stomach for too long, its acidity converts it to creatinine. It therefore decomposes into a waste material which the body has to break down and excrete via the liver and kidneys. Here the creatine-alkalyn is supposed to slow down this conversion and channel the creatine safely through the gastric tract.
- Creatine CEE
With this creatine, another molecule is attached to the creatine with the so-called ester. Esters are organic compounds formed by the esterification, a reaction of carboxylic acid and alcohol. Esters are found in adipose tissue and can be used by the body to transport active ingredients into the cells. This principle of absorbing nutrients is intended to help the creatine to enter the muscle cells faster and better. The following advantages are associated with creatine CEE: There is no water retention in the muscle; is suitable for so-called non-responders.
creatine quality
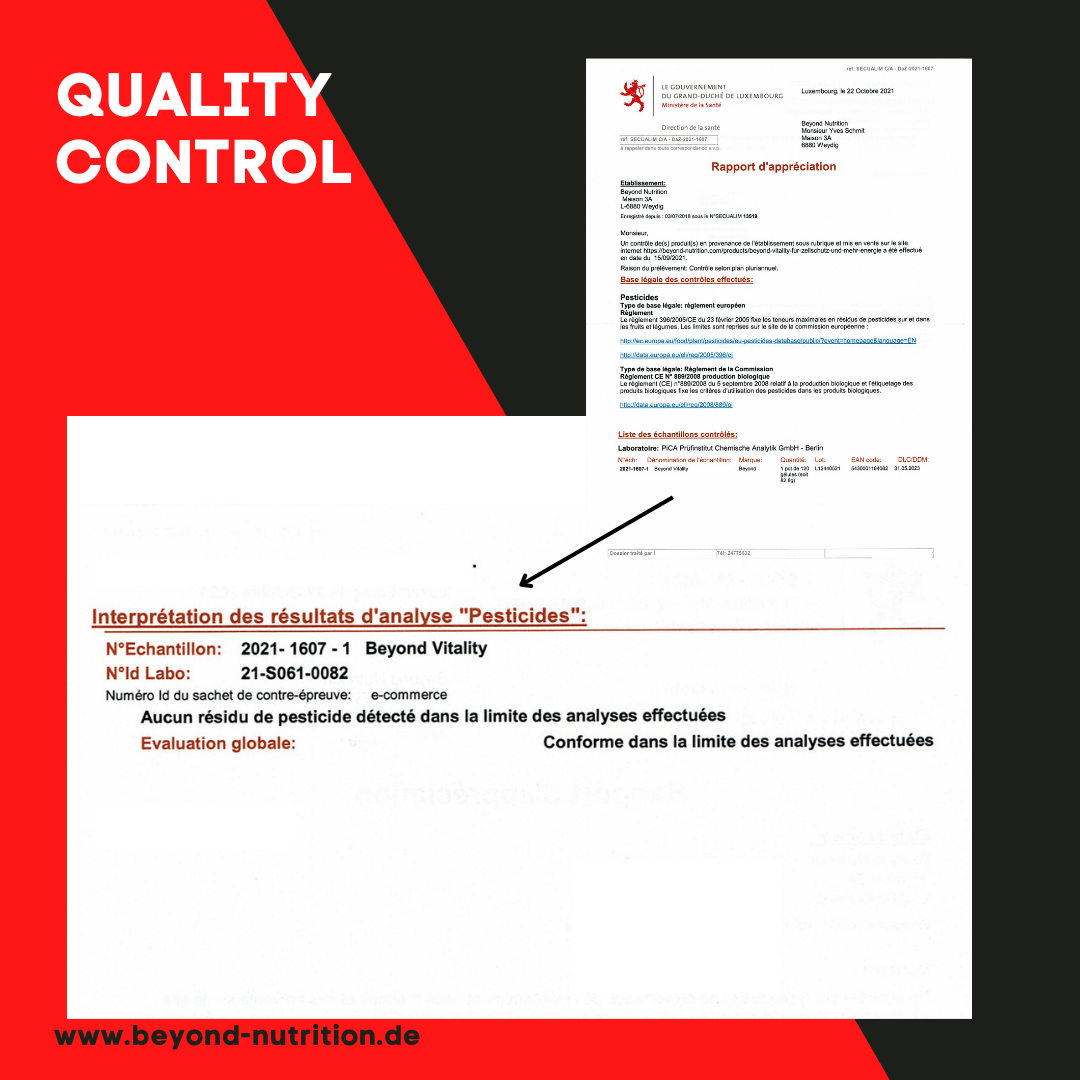
When choosing the right creatine, quality plays a crucial role. If possible, the creatine should not come from third countries. Creatine from China in particular has made headlines in recent years due to contamination.
In 44% of the samples the creatinine level was over 100mg/kg. 15% of the samples had increased levels of the harmful substances dicyandiamide (DHT)!
However, how do I recognize a good creatine?
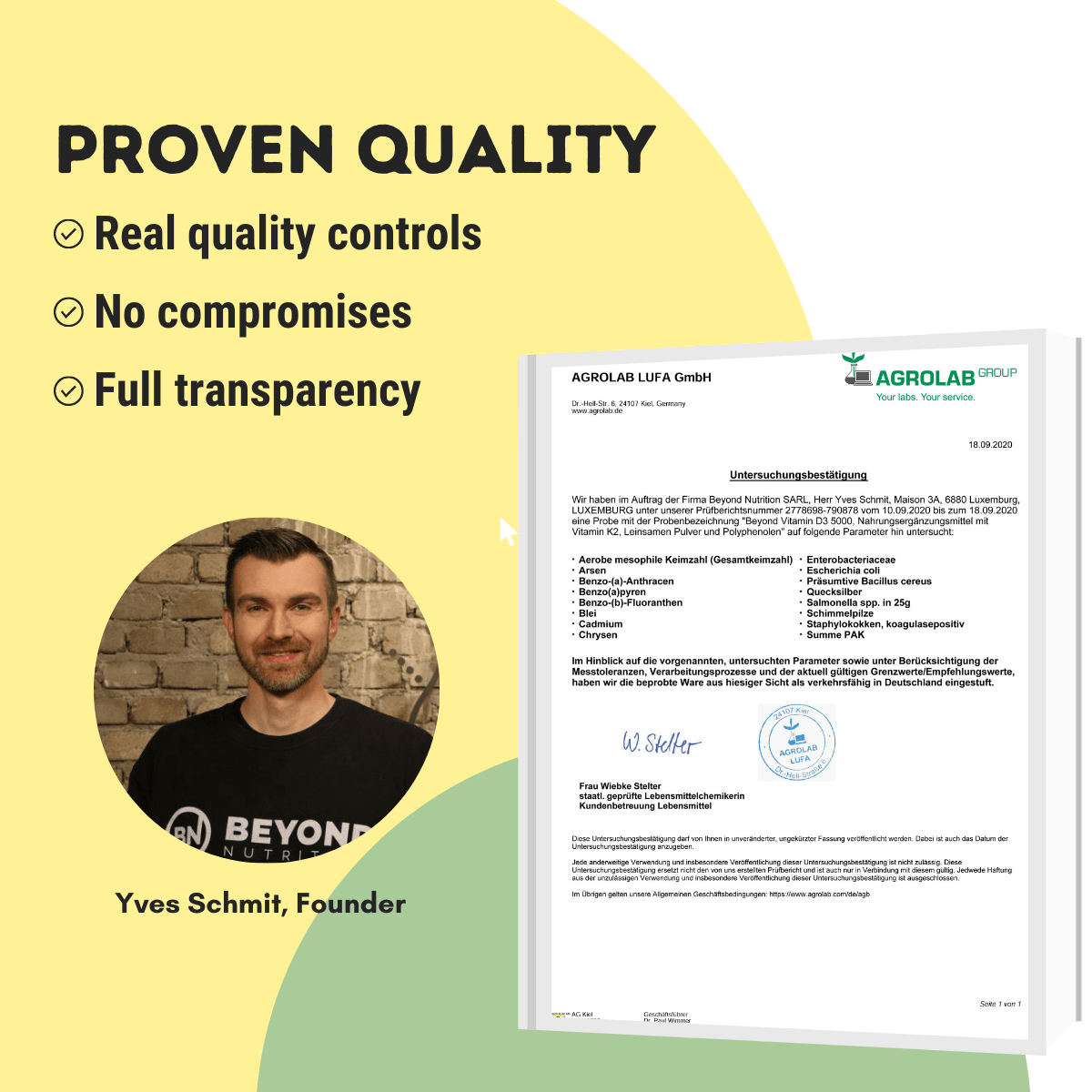
First you have to find a manufacturer that gives you the necessary trust and transparency. This in particular in terms of production, data sheets and laboratory analyses. Products should come from well-known and certified manufacturers. Recognized quality seals such as the "Creapure" made in Germany are symbols of high quality standards.
The following characteristics characterize a good creatine:
- High purity > 99% creatine
- Fine, easily soluble powder (mesh factor > 79)
- Low creatinine level <60mg/kg
- Low DHT level <3mg/kg
- Low DCD <50mg/kg
Laboratory analyzes and certificates also provide a good insight. However, many manufacturers do not provide these. Attached is the Beyond Creatine Certificate of Analysis for your convenience.
Link to the laboratory results from Beyond CreaPro
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has issued an opinion on this. You can find more information about the creatine guidelines of the EU here:
EFSA Creatine monohydrate for use in foods for particular nutritional uses.
A large study had dealt with the quality of creatine products a few years ago. 33 samples from different manufacturers were analyzed with some frightening results.
In 44% of the samples the creatinine level (creatine breakdown) was above the threshold of 100mg/kg. The researchers even found increased levels of the harmful substances dicyandiamide (DHT) and dihydro-1,3,5-triazine in 15% of the samples. The only positive thing was that none of the samples showed any heavy metal contamination.
The whole study can be viewed here:
Levels of creatine, organic contaminants and heavy metals in creatine
dietary supplements
When to take creatine - dosage and application
Creatine improves speed and maximum strength and is therefore ideal for strength athletes such as bodybuilders, powerlifters and athletes such as sprinters, swimmers, shot putters or javelin throwers. In general, an intake of 3 to 5 grams per day is recommended.
Of all creatine varieties, the classic monohydrate is considered the most researched form of creatine in the world.
The creatine loading phase is often used, in which up to 20 grams of creatine are taken daily in the first week. This is said to cause a rapid loading of the muscle with creatine phosphate.
Permanent or in cycles?
In the past, creatine was often taken in cycles of 8 to 10 weeks, followed by a longer wait before the next dose. The reason for this is the fact that the creatine stores in the muscles are limited. Once this has reached its maximum capacity, no more creatine can be stored.
Creatine is now being taken more and more frequently. A daily dose of 3 g is used here. Long-term studies have not been able to determine any negative effects from long-term use, provided the athletes are in perfect health.
Our opinion on creatine intake
In this case, we at Beyond Nutrition are rather "old school" and recommend taking it in cycles of up to a maximum of 10 weeks. We would also do without a loading phase, it is not needed to load the creatine stores in the muscle. The now increased creatine buffer in the muscle will remain elevated for several weeks after ingestion. The body regenerates the creatine itself or absorbs it from food.
Creatine Non-Responders - not for everyone
Creatine non-responders are people who do not experience a noticeable increase in performance when taking creatine. It is believed that approximately one in five is affected. This can have several causes.
On the one hand, there are people who already have a high proportion of creatine in their muscles, so the effect of additional intake is very small. This can be influenced by genetics and the daily food we eat. If this is already rich in foods containing creatine, additional intake would make little sense. This is because, as already mentioned, the memory in the muscle is limited.
On the other hand, your body's receptiveness may be limited. Again, there can be multiple causes ranging from genetics, the condition of the digestive tract (creatine is absorbed in the small intestine) to absorption in the cell walls.
Finding the right remedy is often difficult, and creatine products in connection with a so-called transport matrix are often ideal here.

Creatine with transport matrix
Most of the absorption of creatine occurs in the small intestine, but in order to get there, creatine must first pass through the acidic stomach. However, this has major disadvantages because a proportion of the creatine decomposes in the stomach acid and breaks down into the harmful by-product creatinine, which is then absorbed and broken down by the liver.
To counteract this effect, modern creatine supplements contain a so-called creatine transport matrix. This should optimize the passage through the stomach, improve absorption and strengthen the infiltration into the muscle cells.
A transport matrix usually consists of quickly digestible carbohydrates such as sucrose, dextrose and maltodextrin. By absorbing quickly digestible carbohydrates; these are those who have a high glycemic index, the blood sugar level rises. This causes the pancreas to release more insulin. Along with testosterone and growth hormone (HGH), insulin is one of the most anabolic hormones of all. It literally smuggles the nutrients into the muscle cells. This effect is particularly popular post-workout to counteract the catabolic state. Many post-workout shakes contain quickly digestible carbohydrates. However, the post-workout shake theory has never been scientifically proven. Outside of the training time, however, you should try to keep your insulin level constant.
- creatine and magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral. Its role in the body is well known to many athletes. Magnesium supports muscle function and that of the nervous system. It is important to know that physical exertion not only demands muscles but also the nervous system. Like creatine, magnesium is absorbed in the intestine and is therefore an ideal supplement to creatine. In one study, a combined intake of both nutrients led to increased cellular fluid absorption. The assumption is so obvious that more creatine was stored in the muscles. This can have a positive effect on athletic performance and regeneration.
Study:
Magnesium-creatine supplementation effects on body water
- creatine and beta-alanine
At Beta-Alanine It is an amino acid, the precursor to carnosine. Carnosine is a bipeptide and is mainly found in our muscle cells. There it helps the body to break down lactic acid, which occurs during training as a breakdown product when glycogen is broken down. Lactic acid is known to every bodybuilder as the well-known muscle burn.
The performance-enhancing effect of beta-alanine is from "International society of sports nutrition" has been recognized.
If the proportion of lactic acid increases during training, begins the burn muscle. The muscle is then acidic and can no longer perform at its best. Beta-alanine combined with creatine counteracts this process, so creatine increases strength and beta-alanine suppresses lactic acid build-up, allowing for more reps in a set. This in turn leads to more growth stimulus in the muscle and consequently to more muscle growth and improved regeneration through the rapid removal of the lactic acid that has accumulated.
Study:
- Creatine and D-Ribose
D-Ribose is a natural sugar, a monosaccharide, and is converted to energy in cells by activating and stimulating ATP production. After intense physical exertion, the body can benefit from D-Ribose to recharge its energy stores. Especially for sports that train short-term, explosive tension, such as weightlifting, sprinting or strength athletes, Ribose can benefit. It harmonizes very well with creatine and can improve its absorption and effectiveness. For this, both substances should be taken together.
Studies:
The influence of D-ribose ingestion and fitness level on performance and recover.
The role of ribose in human skeletal muscle metabolism
- Creatine and Alpha Lipoic Acid
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) is a sulfur containing fatty acid. In its natural (R) form, it occurs as a coenzyme in the mitochondria and plays an important role in energy metabolism. ALA is also a radical scavenger and powerful antioxidant that can regenerate antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, coenzyme Q10 or glutathione that are used up in the body. Studies have shown that taking creatine and ALA leads to increased creatine concentration in the muscles. ALA promotes the absorption of creatine into the muscle cells, this is promoted by the properties that ALA has as a fatty acid. We have already described a similar principle for creatine CEE.
Studies:
Effect of alpha-lipoic acid combined with creatine monohydrate on human skeletal muscle creatine and phosphagen concentration.Effect of α-Lipoic Acid Combined With Creatine Monohydrate on Human Skeletal Muscle Creatine and Phosphagen Concentration
- Black pepper extract with piperine
pepper is the main alkaloid of black pepper (Piper nigrum) and the carrier of the hot pepper taste. Studies indicate that it can be used as a bioenhancer. Bioenhancers are natural enhancers that are able to increase the bioavailability of active ingredients, nutrients and vitamins. We currently have no studies on the combination of creatine and piperine, but based on studies with other active ingredients, a positive influence on creatine uptake by piperine cannot be ruled out.
More to pepper you can find in ours Beyond Magazine.

final word
Creatine monohydrate is certainly a remarkable natural strength supplement. However, the intake should be coordinated beforehand and only competitive athletes should use it. Only they have the necessary training intensity to take advantage of the extra creatine. For amateur athletes who visit the gym from time to time, it is not necessary to take it.
If you decide to take a creatine supplement, you should definitely make sure that you buy a high-quality product. Cheap creatine can often be contaminated and do more harm than good.
Creatine recommendation for more muscle building:
Our recommendation is definitely that Beyond CreaPro from Beyond Nutrition which is made in Germany. It contains pure creatine monohydrate as well as magnesium and piperine.
With a degree of purity of >99.9%, a maximum creatinine content of 60ppm and a DCD value of less than 20ppm, it is one of the high-quality products on the market. All raw materials are also from purely vegetable sources, ideal for vegans and vegetarians.
Creatine hints
Even though creatine has many benefits and is now considered safe for dosages of up to 5 grams per day, we do not recommend long-term use. An increased level of creatinine in the blood can indicate a saturation of the creatine content in the body. As a rule, creatinine values are generally increased in strength athletes, due to the higher creatine synthesis in the muscles. You should consult your doctor or a qualified nutritionist.