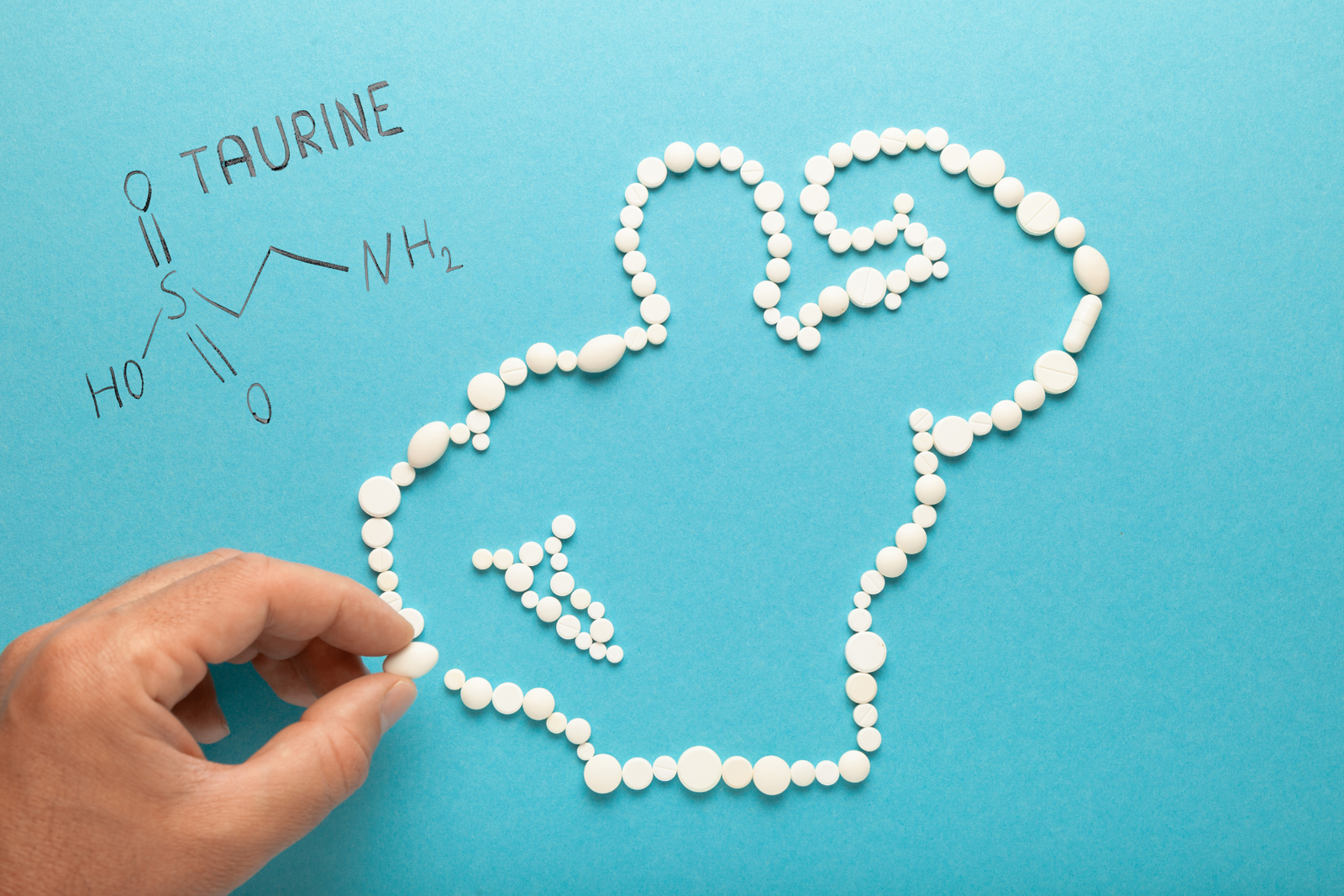
L-Taurine: Everything you need to know about the powerful amino acid

Origin of L-Taurine: The Discovery and Naming
L-Taurine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, was first discovered in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin. They isolated the substance from ox bile and gave it the name taurine, derived from the Latin word "taurus," meaning "bull."
However, it is important to note that taurine is not a classical amino acid, but an amino acid derivative that is structurally different from the classical amino acids. Taurine is formed in the liver from L-cysteine or L-methionine with the participation of vitamin B6. Unlike other amino acids, taurine is not used to build protein in the body and is therefore not proteinogenic.
Nutritional Psychology Aspects of L-Taurine: A Comprehensive Consideration
The nutritional psychological aspects of taurine are diverse, ranging from its role in human nutrition to the health benefits and potential risks of inadequate intake. Taurine is essential to the human body and is found in various body tissues, particularly in the central nervous system, heart muscle and retina of the eye. Although the human body is able to produce small amounts of taurine itself, it is important to get additional taurine from food to meet the need. The estimated daily dose is around 200-400 mg for adults.
Tauine in the diet
Taurine is mainly found in animal foods such as meat, fish and seafood. The concentration of taurine in plant-based foods is significantly lower, which is why vegans and vegetarians should take particular care to consume enough taurine. Some of the richest sources of taurine are beef, lamb, chicken, and seafood such as clams and crab. Dairy products and eggs also contain taurine, but in lower amounts compared to meat and fish.
It is important to note that taurine bioavailability depends on the food in which it is found. Factors such as preparation method, food combination, and the individual's ability to absorb and utilize taurine can affect the amount actually absorbed by the body. To ensure you are getting enough taurine from your diet, it is advisable to eat a balanced and varied diet rich in animal proteins and other sources of taurine.
Insufficient intake of taurine can lead to a variety of health problems, such as impaired cardiovascular function, weakened immune defenses, poorer eye health and impaired cognitive performance. Especially for people who eat vegan or vegetarian food, it can be advisable to increase the taurine intake through dietary supplements (NEM) in order to avoid possible deficiency symptoms.
The numerous benefits of taurine
The numerous benefits of taurine are due to its multiple functions in the human body. In the following some of the most important benefits of taurine are described in detail, here we refer to a large meta study [1] published in 2018 :
- Cardiovascular Support: Taurine may help regulate blood pressure and improve heart function. It supports the contraction force of the heart muscle and thus improves the pumping function of the heart. Taurine also promotes the production of nitric oxide, a molecule responsible for expanding blood vessels. This improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure, which reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Antioxidant effect: Further studies [2] show that tauing, as an antioxidant, protects cells from oxidative stress and free radical damage, which over time can lead to inflammation and chronic disease. Taurine also acts directly on the mitochondria, the cell's energy powerhouses, improving their function and increasing their ability to scavenge free radicals.
- eye health: L-Taurine plays an important role in maintaining the function of the retina and may help prevent age-related eye diseases such as macular degeneration and cataracts. It also has a protective effect on the photoreceptor cells responsible for vision, helping to maintain cell integrity and function.
- Stress reduction: Taurine acts as a neurotransmitter and modulator in the central nervous system and can help reduce stress. It affects the release of stress hormones like cortisol and can help reduce the negative effects of stress on the body. Taurine also promotes the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a calming neurotransmitter substance that helps balance the nervous system and promote relaxation.
- Muscle building and regeneration: Taurine supports muscle function and promotes regeneration after training. It helps stabilize cell membranes and protect muscle fibers from damage. In addition, taurine can improve the absorption of calcium in the muscles, which leads to better contraction strength and endurance. Finally, taurine promotes the release of growth hormones, which are essential for muscle building and repair.
Taurine in everyday life: application and dosage for optimal results
Taurine can be incorporated into your daily routine in a number of ways to reap its health benefits. Here are some tips on how to use and dose taurine effectively:
- Dietary supplements: Taurine is available as a NEM in various forms, such as e.g. B. in capsules, tablets or powder. The recommended daily dose for adults is between 200-400 mg. If in doubt, consult a doctor or nutritionist to determine the appropriate dose for you.
- Nourishment: Eating a balanced and varied diet rich in sources of taurine can help ensure you get enough taurine from your food. Be sure to include animal proteins such as meat, fish and seafood, as well as dairy and eggs in your diet. Vegans and vegetarians should specifically look for plant-based sources of taurine.
- Sports and regeneration: According to studies [3], taurine supports muscle function and promotes recovery after exercise, it makes sense to integrate taurine into your training routine. You can take taurine supplements before or after your workout to benefit from its muscle building and recovery properties. The ideal dosage can vary, so it's a good idea to speak to your trainer or nutritionist to determine the amount that's right for you.
- Stress management: Taurine can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. You can take taurine supplements during times of stress or as part of your daily routine to benefit from its calming effects. The recommended dosage may vary based on individual needs, so it's important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and seek expert advice if needed.
L-Taurine supports brain function and cognitive performance
Taurine plays another role in promoting brain function and cognitive performance. An amino acid found in high concentrations in the brain, taurine works in a variety of ways to support cognitive abilities such as memory, concentration, and learning ability. The various mechanisms by which taurine supports the brain and cognitive functions are explained in detail below.
First, taurine functions as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in the central nervous system. By regulating the release and action of other neurotransmitters, such as GABA and glutamate, taurine helps maintain neuronal excitability and signaling between nerve cells. A balanced neurotransmitter balance is crucial for good brain function and cognitive performance.
Taurine also acts as an antioxidant in the brain, where it protects nerve cells from the damaging effects of free radicals and oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can lead to impaired brain function and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. By protecting cells from damage, taurine helps maintain healthy brain function and cognitive performance over time.
Taurine also has neuroprotective effects by stabilizing cell membranes and maintaining cell integrity. This is important for signaling and communication between nerve cells, which are crucial for cognitive functions such as memory and learning. In addition, taurine supports the formation of new nerve cells and synaptic connections in the brain, a process known as neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity. This promotes the brain's ability to learn and adapt, and helps improve cognitive performance.
Finally, taurine promotes blood flow to the brain by increasing the production of nitric oxide, which dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow. Good blood flow is critical to providing the brain with the oxygen and nutrients it needs for optimal functioning and cognitive performance.
Overall, taurine supports brain function and cognitive performance in a variety of ways, making it an important amino acid for maintaining mental health and vitality. By integrating taurine-containing foods or supplements into your everyday life, you can benefit from these cognitive benefits and keep your brain healthy and efficient. It's important to note that a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are also crucial to supporting brain function and cognitive performance. Combined with a healthy lifestyle, L-Taurine can help improve your mental performance and protect your brain from age-related changes and diseases over time.
Conclusion: L-taurine for health and well-being
Taurine is a powerful amino acid derivative with many health benefits. By incorporating taurine into your diet and using supplements where necessary, you can support your cardiovascular health, eye health, stress reduction and muscle function. Eat a balanced diet to meet your taurine needs and speak to an expert if you have any questions or concerns.
Sources
[1] Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent
Study [Link]
[2] The Role of Taurine in Mitochondria Health: More Than Just an Antioxidant
Study [Link]
[3] Taurine in sports and exercise
Study [Link]